Surfactants 101
Sea-Land Chemical Company |
What is a Surfactant
A Surfactant or surface active agent is a compound that lowers the surface tension or interface tension of a fluid. Surfactants are added to affect the wetting, dispersing, emulsifying, or cleaning benefits of a product.
market trends for 2023
- Eco and consumer-friendly
- Single package/ pod dosing
- Super concentrates
- Buying habits affected by inflation
- Products with extended life properties
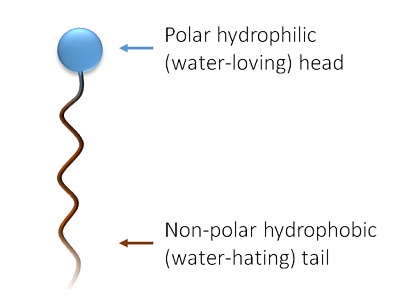
Surfactant Basics
A surfactant is effective due to its shape and charge. The negatively charged, hydrophobic tail is attracted to surrounding dirt and oils. The positively charged hydrophilic head lifts and suspends soils into the water to wash the dirt from the surface.
4 families of Surfactants
There are four families of Surfactants:
- Anionic
- Ionized in an aqueous solution
- Carries a negative charge
- Phosphates, sulfonates, sulfates
- Cationic
- Ionized in an aqueous solution
- Carries a positive charge
- Quaternary ammonium
- Amphoteric
- Ionized in an aqueous solution
- Carries positive or negative charge based on the pH
- Betaines
- Non-Ionic
- Non-ionized in aqueous solution
- Ethoxylated or non-ethoxylated
Surface Tension
The surface tension of a liquid is a measure of the cohesive forces that hold the molecules together. It is the tendency of the liquid to maintain its shape and shrink into the minimum surface area possible with minimum contact.
Surfactants influence the dynamic behavior of surface tension. They help to lower the surface tension interaction which helps to increase wetting.
HLB Testing
HLB stands for Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Balance and is the relationship between hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfactants when forming an emulsion. It was developed specifically for ethoxylated, non-ionic surfactants and based on a 1-20 scale. The higher the HLB number, the more hydrophilic the surfactant and the lower the number, the more hydrophobic/lipophilic.
Oils will have two required HLB’s to achieve an emulsion, lower required HLB’s typically in the 4-6 range for invert emulsions, (W/O) and higher required HLB’s in 8-12 for normal, O/W emulsion.
To form a stable emulsion match the required HLB of the oil with the HLB of the emulsifier(s).
Surfactant Applications:
Surfactants are used in various cleaning applications including, but not limited to:
- Car care
- Laundry Care
- Hard surface cleaners
- Dish care
- Deodorizers and disinfectants
- Floor care